Conquering the Stairway to Safety: Your Guide to Interior Handrail Building Codes
Ever tripped going up the stairs? A seemingly minor stumble can quickly become a dangerous fall. That's where interior stair handrail building codes come in. These regulations aren’t just arbitrary rules; they’re vital safety measures designed to protect you and your loved ones. This comprehensive guide will unravel the complexities of handrail codes, ensuring you have all the information you need to build or renovate your staircase safely and legally.
Navigating the world of building codes can feel overwhelming, but understanding the regulations surrounding interior stair handrails is crucial for any homeowner or builder. These codes are designed with a singular purpose: to prevent falls and ensure the safety of everyone using the staircase. By adhering to these guidelines, you’re not just complying with the law, you're actively investing in the well-being of those in your home.
Historically, stair-related accidents have been a significant cause of injury, prompting the development of standardized building codes. Early handrail requirements were rudimentary, focusing on basic structural integrity. Over time, these codes evolved, incorporating ergonomic considerations, accessibility guidelines, and more stringent safety measures. Today, modern building codes for interior stair handrails are far more comprehensive, addressing various aspects of design and construction.
The core issues addressed by interior stair handrail building codes revolve around safety and accessibility. Regulations dictate factors like handrail height, graspability, continuity, and structural strength. These stipulations ensure handrails provide adequate support, prevent falls, and assist individuals with mobility challenges. Ignoring these critical components can lead to dangerous staircases that pose significant safety risks.
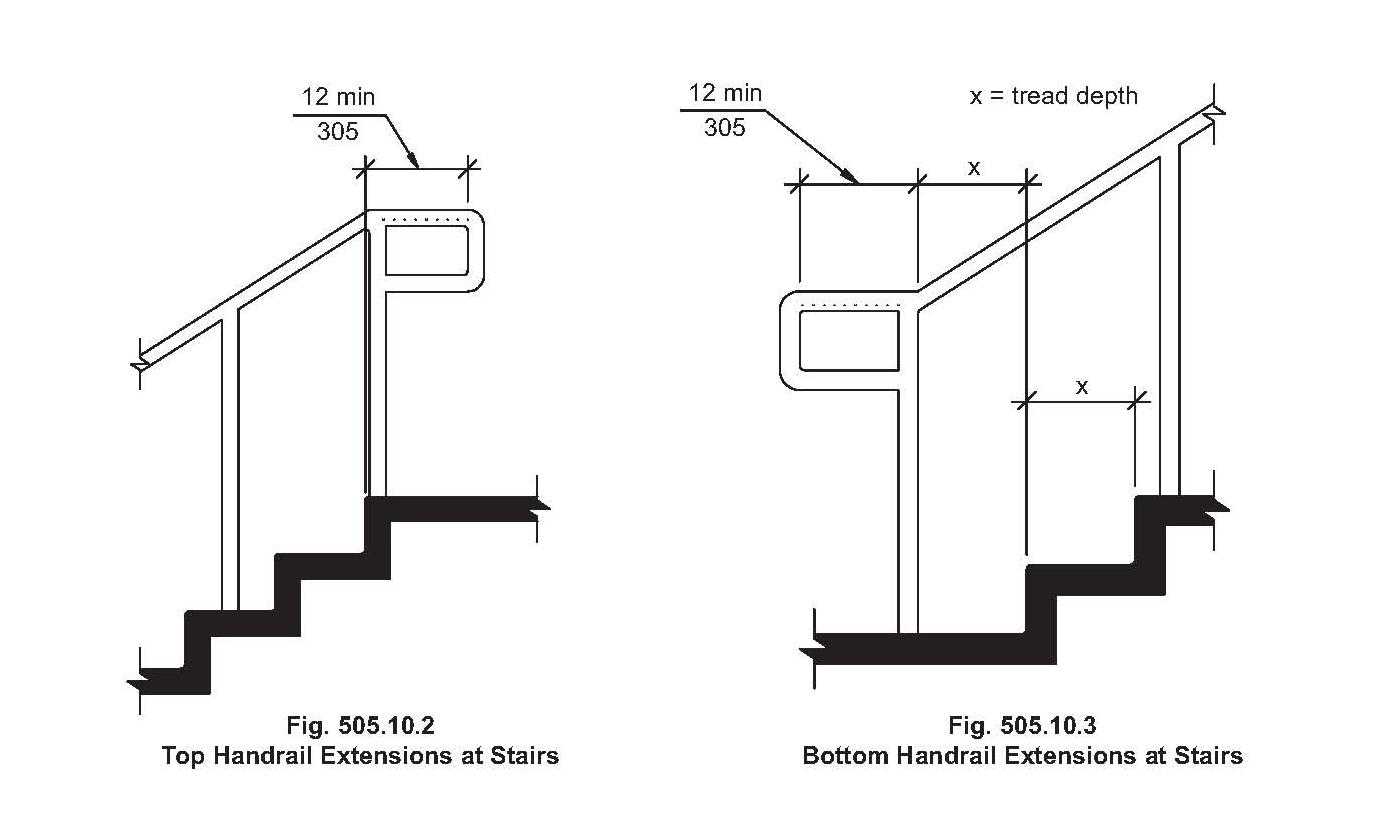
Understanding the terminology surrounding handrail codes is essential for proper implementation. "Graspability," for example, refers to the handrail's ability to be firmly gripped. This typically involves adhering to specific diameter and profile requirements. "Continuity" dictates that the handrail should extend continuously along the entire length of the stair flight, without interruptions or abrupt changes in height. These specific parameters, outlined in the building codes, work together to ensure optimal handrail functionality and user safety.
One significant benefit of adhering to handrail building codes is enhanced safety. By following these regulations, you minimize the risk of falls, protecting both residents and visitors. Another advantage is increased accessibility. Properly designed handrails provide crucial support for individuals with mobility impairments, elderly individuals, and children, allowing them to navigate stairs with greater ease and confidence. Finally, compliance with building codes can increase your home's value. A staircase built to code signifies quality construction and a commitment to safety, making your property more attractive to potential buyers.
An effective action plan for ensuring handrail code compliance begins with researching your local building codes. These regulations can vary depending on your geographical location, so it’s crucial to consult the specific requirements for your area. Next, engage a qualified contractor or inspector to assess your staircase and ensure it meets all applicable codes. Finally, maintain your handrails regularly, checking for any loose components or damage that could compromise their safety and functionality.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Strict Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Increased Construction Costs |
| Improved Accessibility | Design Limitations |
| Enhanced Property Value | Potential for Over-Regulation |
Best practices for implementing handrail building codes include using appropriate materials, ensuring proper installation, and conducting regular inspections. Employing durable and weather-resistant materials ensures the handrail’s longevity and structural integrity. Precise installation, following manufacturer's instructions and local codes, guarantees the handrail's functionality and safety. Routine inspections help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Where can I find my local building codes? Check your local government's website or contact your building department.
2. What is the standard handrail height? This varies, but typically falls between 34 and 38 inches.
3. Do I need a handrail on both sides of the staircase? Usually, yes, especially for staircases wider than a certain measurement.
4. What materials are acceptable for handrails? Wood, metal, and composite materials are common choices.
5. Can I install a handrail myself? While possible, it’s recommended to hire a qualified professional.
6. How often should I inspect my handrails? At least annually, or more frequently if there's heavy usage.
7. What are the penalties for not complying with handrail codes? These can include fines and legal action.
8. Are there exceptions to handrail codes? There might be, particularly in historic buildings, but it's important to consult with local authorities.
A simple tip for ensuring handrail compliance: measure twice, install once. Accurate measurements are crucial for meeting code requirements and ensuring the handrail's functionality.
In conclusion, adhering to interior stair handrail building codes is not just a legal obligation—it's a fundamental aspect of home safety. By understanding these regulations and implementing them effectively, you're creating a safer and more accessible environment for everyone. From preventing falls to increasing property value, the benefits of complying with handrail codes are undeniable. Take the necessary steps to ensure your staircase meets all applicable standards and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with knowing your home is both beautiful and safe. Don’t compromise on safety – invest in compliant handrails today and make your stairs secure for years to come. By prioritizing safety and accessibility, you create a home that is truly welcoming and secure for everyone who enters it.
Wheel nut wisdom conquer torque wrench settings like a pro
Discovering oak hill wvs rail trail gem
Unpacking tucker carlson the pursuit of truth













:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-final-CJ-01-157768d7ac40439da36f9ba69faa00c6.png)