Decoding Circuit Symbols: The Key to Electrical Literacy
Ever wondered how those cryptic lines and squiggles on electrical diagrams translate into functioning gadgets and power grids? The answer lies in understanding open and closed circuit symbols, the fundamental language of electrical engineering. These visual representations are the building blocks of circuit design, conveying crucial information about the flow of electricity.
From the simplest light switch to the most complex computer motherboard, circuit diagrams rely on standardized symbols to depict various components and their connections. Mastering these symbols is like learning the alphabet of electronics, enabling you to decipher complex systems and troubleshoot electrical problems.
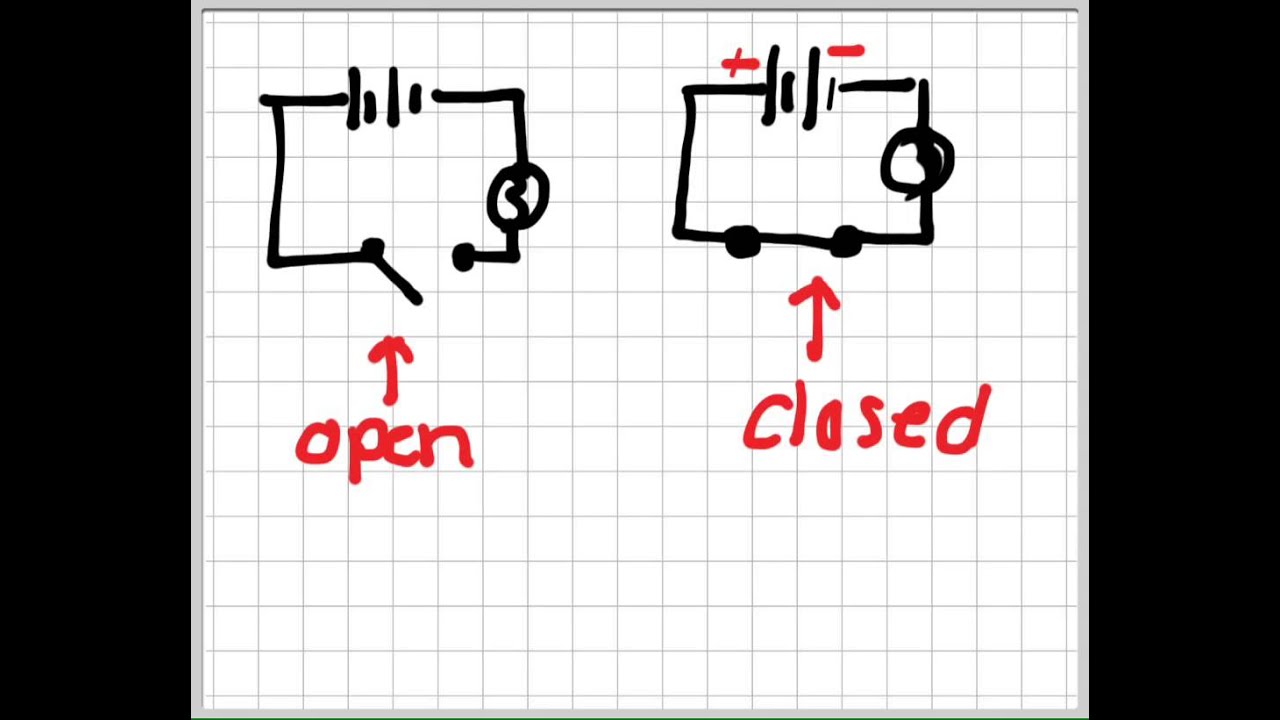
Open circuit symbols represent a break in the electrical pathway, preventing the flow of current. Imagine a light switch in the "off" position – it creates an open circuit, halting the flow of electricity to the bulb. Conversely, closed circuit symbols denote a complete, unbroken pathway, allowing current to flow freely. Flipping the light switch to the "on" position closes the circuit, illuminating the bulb.
The history of these symbols is intertwined with the development of electrical engineering itself. As the field progressed, the need for a universal visual language became apparent. Standardization efforts led to the creation of a consistent set of symbols, enabling engineers worldwide to communicate effectively.
These symbols are not merely abstract representations; they are powerful tools for analysis and problem-solving. By visualizing the flow of electricity through a circuit diagram, engineers can identify potential issues, optimize designs, and ensure the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems.
Open and closed circuit states are fundamental concepts in electricity. An open circuit implies no current flow due to a break in the conductive path. A closed circuit allows uninterrupted current flow through a complete pathway. For example, a simple circuit with a battery, switch, and light bulb demonstrates these states. With the switch open (off), the circuit is open, and the bulb stays off. Closing the switch (on) completes the circuit, allowing current to flow and the bulb to light up.
Benefits of understanding these symbols include: enhanced troubleshooting abilities, simplified circuit design interpretation, and improved communication among electrical professionals. For instance, recognizing an open circuit symbol on a diagram can quickly pinpoint a broken wire or faulty component. Being able to interpret closed circuit pathways helps understand how current flows through interconnected components.
To create a simple circuit, gather a battery, a light bulb, wires, and a switch. Connect the positive terminal of the battery to one side of the switch. From the other side of the switch, run a wire to the bulb, and connect the other terminal of the bulb back to the negative terminal of the battery. This forms a basic circuit. Opening the switch creates an open circuit, while closing it creates a closed circuit.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Circuit Symbol Knowledge
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved Circuit Analysis | Requires Initial Learning |
| Effective Troubleshooting | Can be Complex in Advanced Circuits |
| Clear Communication | Variations in Symbol Standards |
Best Practices for using circuit symbols include adhering to standard conventions, using clear and concise diagrams, labeling components appropriately, and verifying designs before implementation.
Real-world examples of open and closed circuits are abundant. A doorbell uses a closed circuit to activate the chime when the button is pressed. A faulty light fixture might have an open circuit due to a broken wire. A car's ignition system uses a closed circuit to start the engine. A power outage effectively creates an open circuit, interrupting the flow of electricity to homes and businesses. A flashlight uses a closed circuit to illuminate the bulb when switched on.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between an open and closed circuit? - An open circuit has a break, preventing current flow; a closed circuit allows current to flow.
2. Why are circuit symbols important? - They provide a standardized visual language for understanding electrical systems.
3. How do I identify an open circuit in a diagram? - Look for a break in the conductive path, indicated by a specific symbol.
4. What happens when a circuit is closed? - Current flows through the complete pathway.
5. What causes an open circuit? - A broken wire, faulty component, or an open switch.
6. How do I create a simple closed circuit? - Connect a power source, wires, and a component like a light bulb in a continuous loop.
7. Where can I learn more about circuit symbols? - Textbooks, online resources, and educational apps offer valuable information.
8. How can understanding circuit symbols help me in everyday life? - It allows you to troubleshoot basic electrical issues and understand how electrical devices operate.
Tips and tricks for working with circuit diagrams include using simulation software to test designs, practicing drawing common symbols, and referring to reference guides when encountering unfamiliar symbols.
In conclusion, understanding open and closed circuit symbols is crucial for anyone working with or interested in electrical systems. These seemingly simple representations are the key to unlocking the complexities of circuit design, troubleshooting, and analysis. By mastering these fundamental building blocks, you empower yourself to navigate the world of electronics with confidence. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or a curious beginner, the ability to interpret these symbols opens doors to a deeper understanding of how electricity shapes our modern world. Exploring the rich history and diverse applications of these symbols reveals their profound impact on technological advancement. By actively engaging with these concepts, you contribute to a greater appreciation for the intricate workings of the electrical systems that power our lives. Embrace the challenge of learning these symbols and unlock the potential for innovation and problem-solving in the exciting world of electronics.
Navigating medicare supplement plans a smart comparison
Unlocking the world of football ea sports fc 24 leagues
Understanding bona fide agricultural purposes