Decoding Stair Railing Regulations: Safety, Standards, and Design
Ever tripped on a staircase? It's a jarring experience, a sudden reminder of the crucial role handrails play in our everyday safety. Beyond mere convenience, stair railing regulations are a complex network of building codes, safety standards, and accessibility guidelines, all working in concert to minimize the risk of falls and ensure safe navigation. This deep dive explores the intricacies of these regulations, unpacking the "code" behind secure and compliant handrails.
Understanding stair railing requirements isn't just about ticking boxes on an inspection checklist; it's about creating safe environments. From public spaces to private residences, these regulations impact architects, builders, homeowners, and anyone involved in designing, constructing, or maintaining staircases. The seemingly simple handrail is, in fact, a critical safety feature governed by strict guidelines designed to protect users.
The historical evolution of handrail regulations reflects a growing awareness of safety and accessibility. Early building codes often lacked specific requirements, leaving handrail design largely to individual discretion. However, as the understanding of fall risks and accessibility needs increased, so did the need for standardized regulations. This led to the development of comprehensive codes like the International Building Code (IBC) and other regional variations, which provide detailed specifications for handrail height, strength, materials, and other critical aspects.
One of the central issues regarding handrail regulations is ensuring consistent implementation. Variations in local codes, differing interpretations, and the challenge of retrofitting existing structures can lead to inconsistencies in handrail design and installation. This highlights the importance of clear communication, thorough training, and ongoing inspection to maintain consistent compliance and ensure maximum safety.
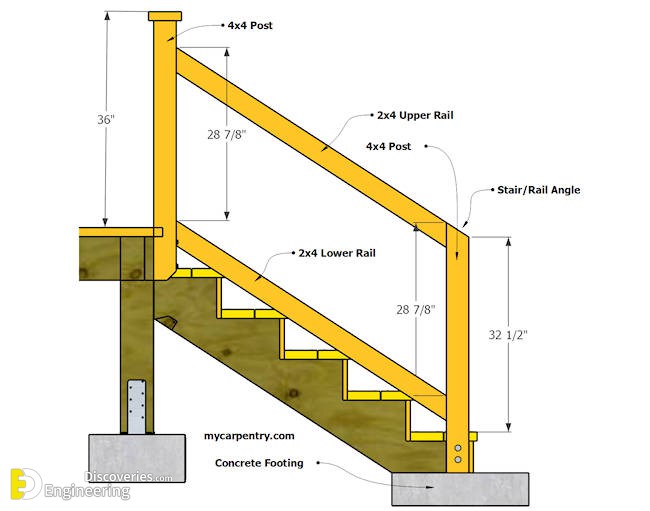
Handrail codes are primarily concerned with dimensions and structural integrity. Key parameters include handrail height, typically measured from the nosing of the stair treads, as well as the cross-sectional dimensions of the handrail itself to ensure a comfortable and secure grip. Regulations also dictate the strength and load-bearing capacity of handrails, ensuring they can withstand the weight of a person leaning or falling against them. Materials used in handrail construction are also subject to scrutiny, with specific requirements for durability, fire resistance, and resistance to corrosion or decay.
Benefits of adhering to handrail codes are multifaceted. Firstly, and most importantly, compliant handrails significantly reduce the risk of falls, particularly among children, the elderly, and individuals with mobility impairments. Secondly, adherence to code ensures legal compliance, protecting builders and homeowners from potential liabilities. Thirdly, properly designed handrails enhance the overall aesthetic of a staircase, adding a touch of elegance and functionality to the space.
Developing an action plan for handrail compliance starts with understanding the relevant local codes and regulations. Consulting with a qualified architect or building inspector can provide valuable insights into specific requirements. Accurate measurements and careful planning are crucial for a successful installation. Regular inspections and maintenance are also essential for ensuring long-term compliance and safety.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Can be costly to implement, especially in retrofits |
| Legal Compliance | May limit design flexibility in some cases |
| Improved Accessibility | Local code variations can create confusion |
Best practices for handrail implementation include ensuring continuous handrails along the entire length of the staircase, avoiding any abrupt changes in height or direction. Securely anchoring handrails to the supporting structure is crucial, as is using appropriate fasteners and materials. Regular inspections and maintenance should be conducted to identify and address any wear and tear or damage.
Challenges in implementing handrail regulations can include dealing with complex geometries, particularly in spiral or curved staircases. Integrating handrails into existing structures can also present difficulties, especially when retrofitting older buildings. Finding qualified installers with expertise in handrail regulations can also be a challenge. Solutions to these challenges include careful planning, collaboration with experienced professionals, and utilizing innovative handrail systems designed for complex applications.
Frequently Asked Questions: What is the standard handrail height? What materials are acceptable for handrails? Are there specific requirements for handrails in commercial buildings? How often should handrails be inspected? What are the penalties for non-compliance? Where can I find local handrail regulations? Who is responsible for enforcing handrail codes? What are the different types of handrail systems available?
Tips and tricks for successful handrail implementation: Always consult with a professional. Invest in high-quality materials. Prioritize functionality and safety over aesthetics. Document all inspections and maintenance activities. Stay informed about changes in local codes and regulations.
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to stair railing regulations is not merely a matter of following the rules, it's a commitment to safety, accessibility, and responsible design. From mitigating fall risks to ensuring legal compliance and enhancing the overall usability of a building, handrails play a vital role in our built environment. By prioritizing compliance and embracing best practices, we can create safer, more accessible, and more inclusive spaces for everyone. The future of handrail design and implementation hinges on a continued focus on innovation, education, and a shared commitment to upholding the highest standards of safety and accessibility. Let's move forward together, building a world where navigating stairs is a safe and confident experience for all.
Suayed unam law curriculum your path to legal success
The dog house season 5 a heartwarming return
Need for speed heat on pc exploring the torrent phenomenon

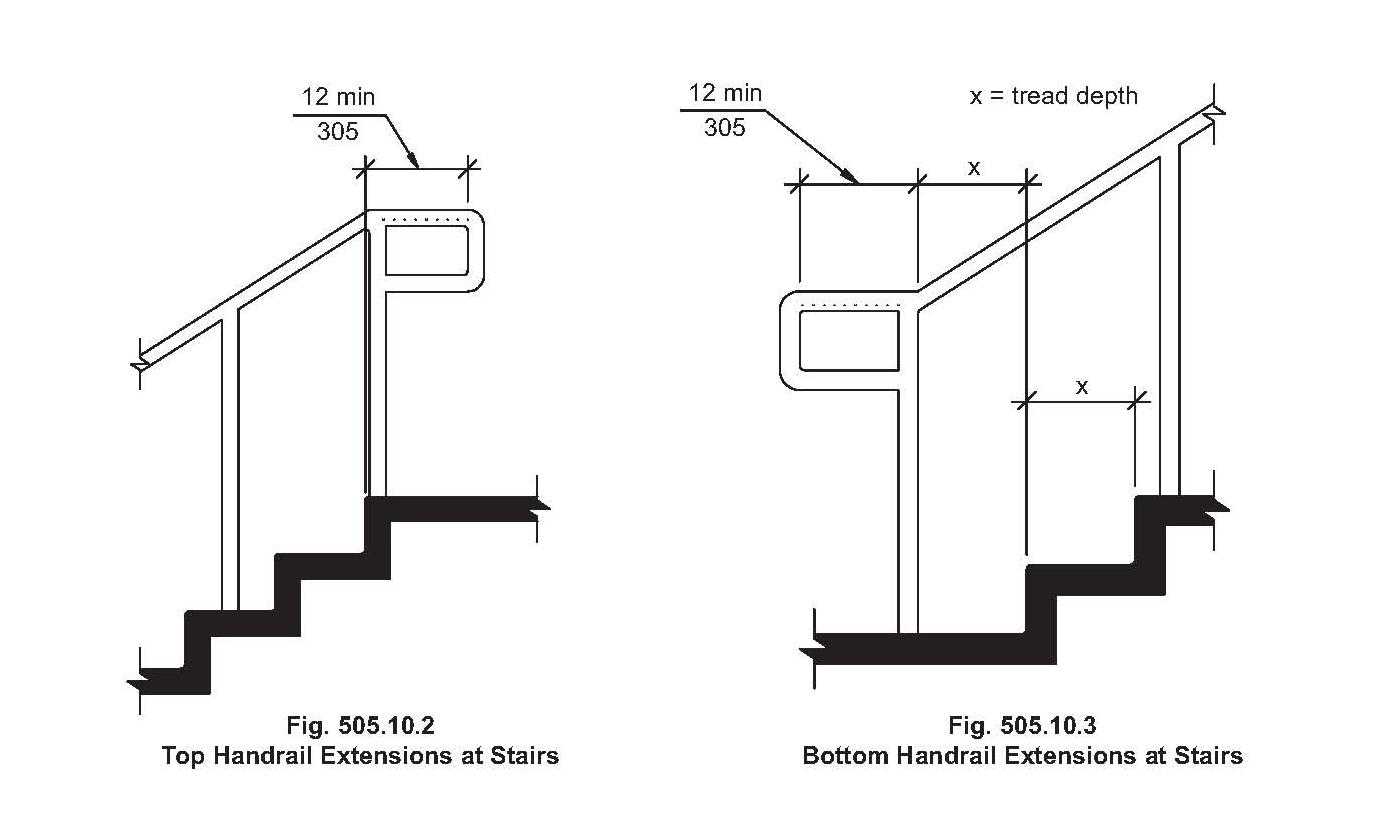









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-FINAL1-5c054b4dc9e77c0001600219.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-final-CJ-01-157768d7ac40439da36f9ba69faa00c6.png)