Decoding Wire Colors The Ultimate Guide to Identified Conductors
Ever found yourself staring at a tangle of wires, wondering what secrets their colorful insulation holds? Understanding the color coding of electrical conductors is crucial, not just for electricians, but for anyone working with electrical systems. This isn't just about aesthetics; it's about safety, efficiency, and ensuring your circuits function correctly. We'll unravel the mystery of "what colour is the identified conductor?" and explore its importance.
The color of an identified conductor provides a visual language for electricians, allowing them to quickly and accurately determine the function of each wire. This system of color-coding isn't random; it's standardized to minimize confusion and prevent potentially dangerous misconnections. Imagine the chaos if wires were all the same color – identifying circuits and troubleshooting problems would be a nightmare.
The history of identified conductor colors can be traced back to the early days of electrical systems. As electrical networks became more complex, the need for a clear identification system became apparent. Early systems may have used arbitrary colors, but standardization eventually emerged, driven by the need for safety and interoperability. This evolution has resulted in the color codes we use today.
The significance of correct conductor identification cannot be overstated. It's the foundation of safe and reliable electrical installations. Misidentifying a wire's function can lead to short circuits, shocks, fires, and damage to equipment. For example, connecting a neutral wire to a live conductor can have disastrous consequences.
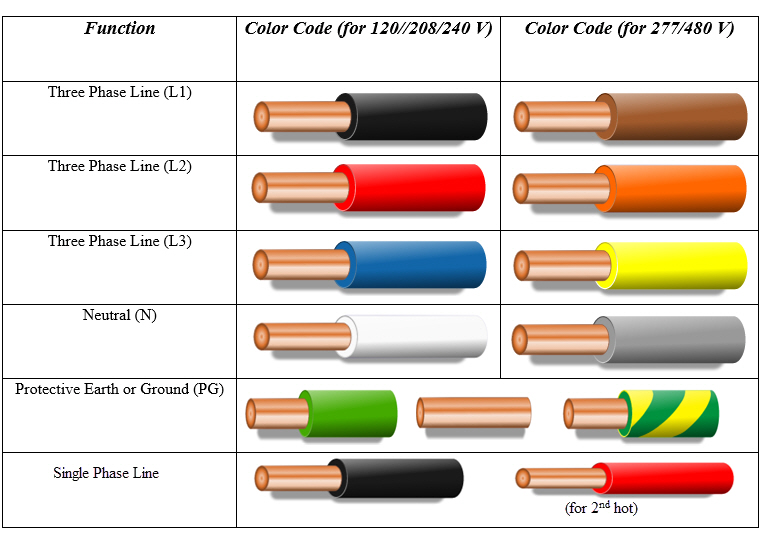
Different regions have adopted variations in color codes for identified conductors. While there are international standards, local regulations often dictate the specific colors used. This underscores the importance of knowing the applicable color code for your region. Resources like the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States or the IET Wiring Regulations in the UK provide detailed guidance.
Let's talk specifics. In the US, according to the NEC, a black wire typically represents a hot wire for power supply. White typically identifies the neutral conductor, completing the circuit and returning current to the source. Green or bare copper wires are used for grounding, providing a path for fault currents to flow safely to the earth.
Understanding these color codes is like knowing the traffic signals of an electrical system. It ensures that the “traffic” of electricity flows smoothly and safely. Think of it as a universal language that ensures electricians worldwide can understand and work with electrical systems efficiently.
Benefits of standardized conductor identification include: enhanced safety by minimizing risks of incorrect connections, simplified troubleshooting by allowing quick identification of circuits and wires, and improved collaboration among electricians working on different parts of a system.
Always consult local electrical codes and regulations when working with electrical wiring. Using a multimeter to verify the function of a wire before making connections is a crucial safety step. Never assume a wire's function based on color alone, especially in older installations where the wiring may not comply with current standards.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Wire Colors
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Variations in regional codes |
| Easier Troubleshooting | Potential for color fading |
| Improved Collaboration | Reliance on color can be misleading in altered systems |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What color is the ground wire? Typically green or bare copper.
2. What does a white wire indicate? Usually neutral.
3. What does a black wire represent? Commonly a hot wire.
4. Do wire colors vary by region? Yes, local regulations can dictate variations.
5. What if a wire's color has faded? Use a multimeter to verify its function.
6. Where can I find information on my local color code? Consult your regional electrical code.
7. Is it safe to assume a wire's function based on color? No, always verify.
8. What should I do if I’m unsure about a wire's identity? Consult a qualified electrician.
In conclusion, understanding “what colour is the identified conductor?” is paramount for anyone interacting with electrical systems. The seemingly simple act of color-coding wires plays a vital role in ensuring safety, simplifying complex wiring installations, and enabling efficient troubleshooting. From preventing potentially fatal shocks to facilitating seamless collaboration among electricians, the significance of standardized wire colors cannot be overemphasized. By learning and respecting these color codes, we contribute to a safer and more reliable electrical world. Remember to always consult your local electrical codes and regulations, and when in doubt, seek the expertise of a qualified electrician. Your safety and the proper functioning of your electrical systems depend on it.
Remembering loved ones hall funeral home obituaries
Aries woman horoscope today ignite your inner fire
Unlocking financial wisdom exploring the work of jeff gerson at morgan stanley