Exploring Water Cooled Heat Pump Condensers
Imagine a world where heating and cooling your home is both efficient and environmentally friendly. That’s the promise of heat pumps, and a key component in maximizing their performance is the condenser. While air-cooled condensers are common, water-cooled heat pump condensers offer distinct advantages in certain situations.
A water-cooled heat pump condenser, in essence, uses water instead of air to dissipate heat. This seemingly simple change has profound implications for energy efficiency, especially in larger buildings or in climates with high ambient temperatures. Think of it like this: when you're trying to cool down a hot pan, running it under cool water is much faster than simply letting it sit in the air.
The journey of heat pump technology, including water-cooled condensers, spans decades. Early systems faced limitations in terms of reliability and efficiency. However, advancements in materials, design, and control systems have transformed water-cooled heat pump condensers into a viable and often superior option for various applications. These systems are now found in everything from large commercial buildings to industrial processes, demonstrating their versatility and effectiveness.
One of the most significant benefits of a water-cooled condenser is its ability to maintain high efficiency even when outside temperatures soar. Unlike air-cooled systems, which struggle to reject heat on hot days, water-cooled systems rely on a consistent water source, allowing them to operate at peak performance regardless of the weather. This translates into lower energy bills and a more comfortable indoor environment.
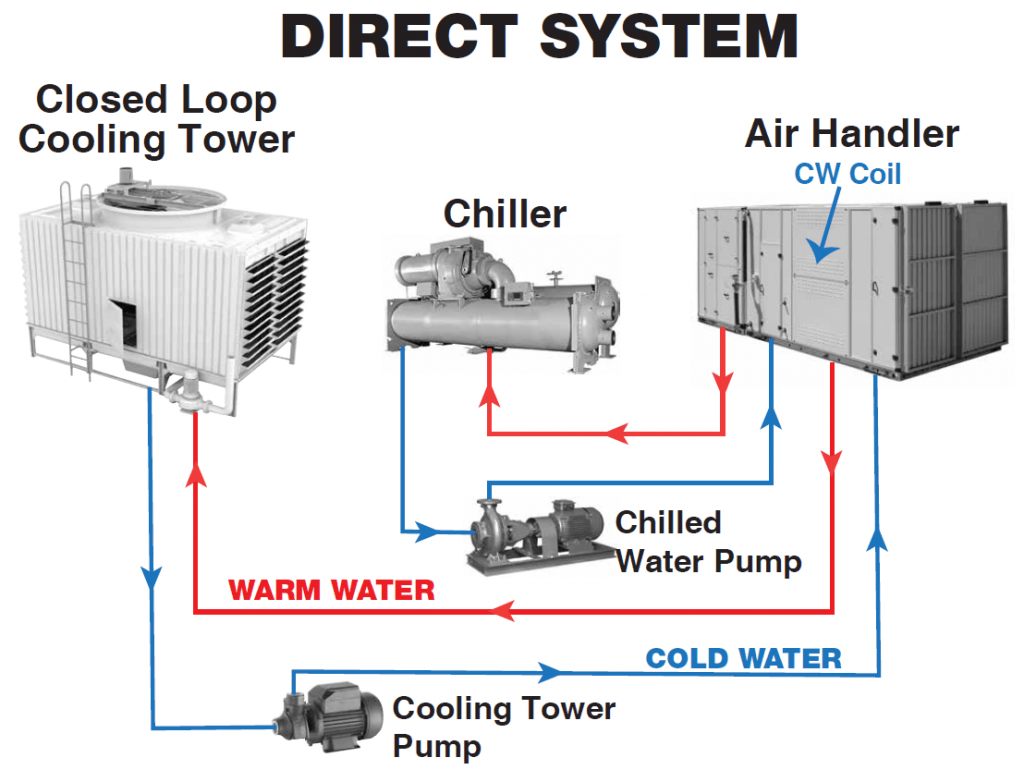
Understanding the workings of a water-cooled heat pump condenser is key to appreciating its value. The condenser receives hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas from the compressor. As this refrigerant passes through the water-cooled coils, the heat is transferred to the circulating water, causing the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid. This cooled liquid then continues through the refrigeration cycle, absorbing heat from the indoor space and repeating the process. The heated water is typically discharged into a cooling tower or other heat rejection system.
Water-cooled condensers offer several advantages: consistent performance in high ambient temperatures, quieter operation compared to air-cooled systems, and potential for heat recovery. For example, the heated water from the condenser can be used for domestic hot water or other heating purposes, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Implementing a water-cooled system requires careful planning and consideration of factors like water availability, piping infrastructure, and maintenance requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Water Cooled Heat Pump Condensers
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Higher efficiency in hot climates | Higher initial cost |
| Quieter operation | More complex installation |
| Potential for heat recovery | Requires a reliable water source |
Best practices for water-cooled heat pump condenser implementation include regular maintenance of the water system, including water treatment to prevent scaling and corrosion, ensuring proper water flow rates, and selecting appropriately sized piping and pumps. Proper insulation of the water lines is also critical to minimize heat loss.
Real-world examples of successful water-cooled heat pump condenser applications include large commercial buildings, district cooling systems, and industrial processes like food processing and pharmaceuticals. Challenges can include water scarcity in some regions and the potential for leaks and water damage. Solutions include using closed-loop systems with minimal water makeup and implementing leak detection and prevention measures.
Frequently asked questions about water-cooled condensers often center around maintenance, water usage, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions about incorporating this technology.
Tips and tricks for optimizing water-cooled heat pump condenser performance include regular inspections of the water system, optimizing water flow rates, and utilizing water treatment strategies to prevent scaling and corrosion. These practices can significantly enhance the lifespan and efficiency of the system.
In conclusion, water-cooled heat pump condensers represent a powerful tool for achieving efficient and sustainable heating and cooling. Their ability to maintain performance in challenging climates, coupled with the potential for heat recovery, makes them a compelling choice for a variety of applications. By understanding the key considerations, benefits, and best practices associated with water-cooled heat pump condensers, you can make informed decisions that contribute to a greener future and optimize your energy consumption. Moving forward, ongoing advancements in heat pump technology promise even greater efficiency and versatility, making water-cooled condensers a key player in the transition towards sustainable building practices and a more comfortable indoor environment. Exploring these options with a qualified HVAC professional can help determine the best solution for your specific needs.
Transforming metal surfaces with johnstones smooth metal paint
Millstone restaurant kings wharf bermuda dining experience
Rutgers university college football a scarlet knight saga