Navigating Medicare Supplemental Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide
Medicare. It's a cornerstone of healthcare for millions of Americans, yet the reality of its coverage often leaves seniors grappling with unexpected expenses. What's the solution? Medicare supplemental insurance, often referred to as Medigap, can help bridge the gaps in Original Medicare coverage, offering a financial safety net for those unforeseen medical costs.
Imagine this: You're enjoying retirement when a sudden illness requires an extended hospital stay. While Medicare covers a portion of the bill, you're left with significant out-of-pocket expenses. This is where supplemental Medicare insurance plans step in. These plans are designed to pick up where Medicare leaves off, covering costs like copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. This added financial security can make a world of difference, providing peace of mind during challenging times.
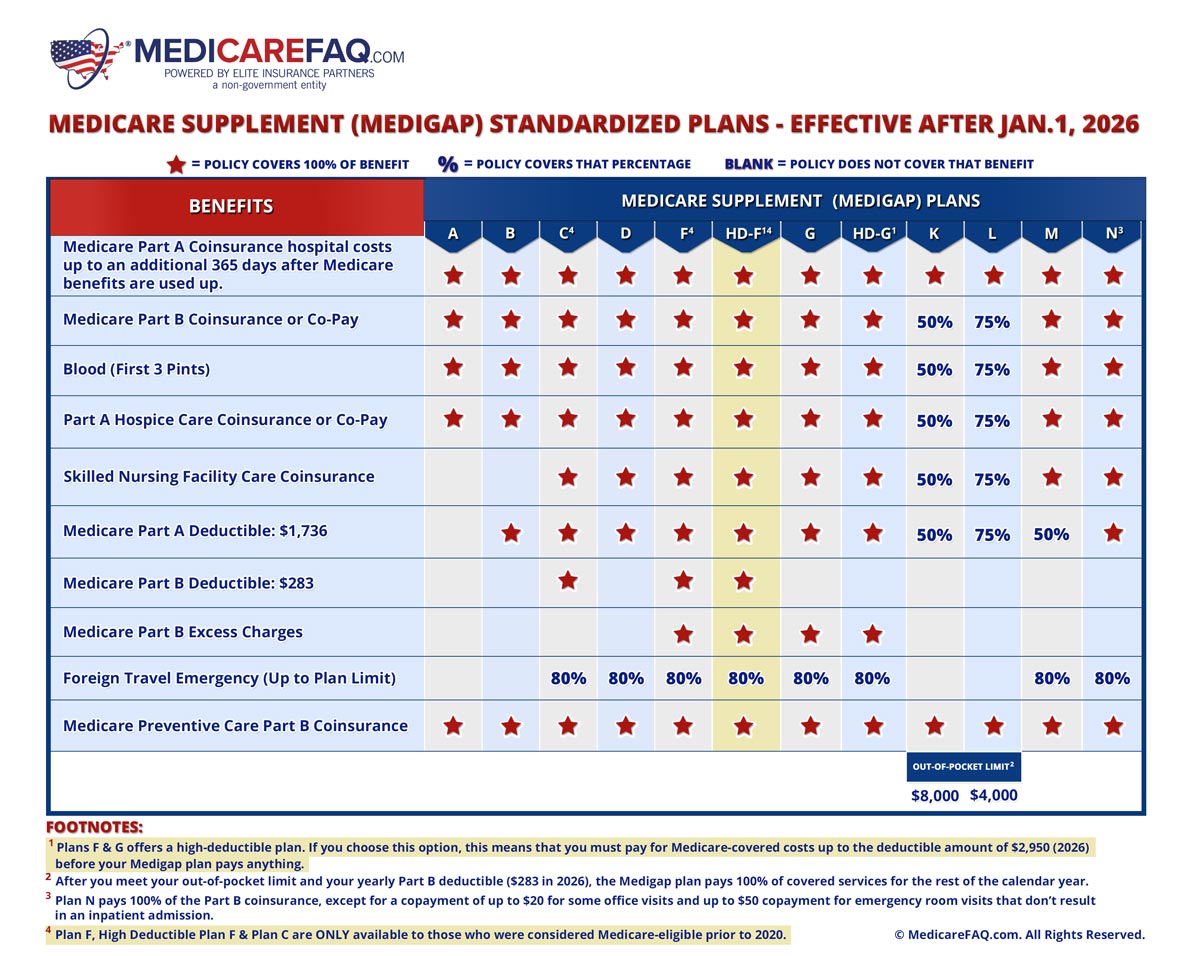
Medicare supplemental insurance isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. Navigating the landscape of available plans can feel overwhelming. There are standardized plans, labeled with letters (like Plan A, Plan G, etc.), each offering different levels of coverage. Understanding these differences is crucial to selecting the right plan to meet your specific needs and budget. Factors like pre-existing conditions and prescription drug coverage play a significant role in this decision-making process.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Medicare supplemental coverage, providing you with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed choices about your healthcare future. From understanding the basics to exploring various plan options and addressing common concerns, we'll cover it all. We'll equip you with the information needed to navigate the complexities of Medigap and secure the coverage that best suits your individual circumstances.
Let's start by exploring the history and evolution of supplemental Medicare insurance. Its development is intricately linked to the evolution of Medicare itself. Recognizing the gaps in Original Medicare coverage, private insurance companies stepped in to offer supplemental plans. These plans are regulated by the government to ensure they meet specific standards, providing consumers with a degree of consistency and transparency when comparing different options.
Supplemental Medicare insurance policies cover costs like copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles that Original Medicare doesn't fully cover. For instance, if you have Plan G, and Medicare covers 80% of a hospital stay, your Medigap plan would cover the remaining 20%, significantly reducing your financial burden.
Benefits of supplemental medicare insurance include predictable healthcare costs, protection against high out-of-pocket expenses, and access to care without referrals for specialists within the Medicare network. For example, a Medigap plan can help cover the costs of a specialist visit, even if your primary care physician didn't refer you.
To choose a plan, evaluate your needs, compare plan benefits and premiums, and consider your budget. You can use online tools from Medicare.gov to compare plans. Consulting with a licensed insurance broker can also provide personalized guidance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Medicare Supplement Insurance
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable Costs | Monthly Premiums |
| Comprehensive Coverage | Limited Coverage for Vision, Dental, and Hearing |
| No Network Restrictions (within Medicare) | Can be Expensive Depending on the Plan and Your Health |
Five Best Practices for choosing Medigap: 1. Review your current healthcare needs. 2. Compare plan benefits and costs. 3. Consider your budget. 4. Consult with a licensed insurance broker. 5. Review your plan annually.
Five Challenges: 1. Cost. Solution: Compare plans and choose one that fits your budget. 2. Understanding plan options. Solution: Use online resources and consult with an expert. 3. Enrollment periods. Solution: Be aware of deadlines. 4. Pre-existing conditions. Solution: Consider plans that offer coverage for pre-existing conditions. 5. Changing needs. Solution: Review your plan annually.
FAQ: 1. What is Medigap? A: Supplemental insurance to cover gaps in Original Medicare. 2. Who is eligible? A: Individuals enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B. 3. How much does it cost? A: Varies depending on the plan. 4. When can I enroll? A: During specific enrollment periods. 5. Can I switch plans? A: Yes, but with potential limitations. 6. Does it cover prescriptions? A: No, consider a Part D plan. 7. What are the different plans? A: Standardized plans labeled A-N. 8. Where can I get more information? A: Medicare.gov.
Tips: Compare plans, understand your needs, and consult with a professional.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of Medicare supplemental insurance can seem daunting, but understanding the available options and choosing a plan that aligns with your individual needs can provide significant financial peace of mind. By carefully evaluating your healthcare requirements, comparing plan benefits, and exploring resources like Medicare.gov and licensed insurance brokers, you can make informed decisions that protect your health and finances. The benefits of predictable costs and comprehensive coverage can significantly enhance your quality of life during retirement, allowing you to focus on enjoying your golden years rather than worrying about unexpected medical expenses. Take the time to thoroughly research your options, seek expert advice, and secure the coverage you need for a healthier, more secure future. Don't wait until a medical emergency arises; take proactive steps today to protect your tomorrow.
Elevate your home with sherwin williams living well
Outboard motor hours deciphered how many is too many
The ultimate guide to mens short haircuts