Safe Steps: Navigating Australian Stair Handrail Regulations
Imagine ascending a flight of stairs, feeling secure and steady with each step. This sense of safety isn't accidental; it's the result of careful design and adherence to building regulations. In Australia, stair handrails are governed by specific codes designed to prevent falls and ensure accessibility for everyone.
Understanding these regulations is crucial for builders, homeowners, and anyone involved in construction or renovation projects involving staircases. Australian stair handrail requirements, outlined primarily in the National Construction Code (NCC), provide a framework for safe and accessible stair design. This includes specifications for handrail height, continuity, strength, and materials.
The National Construction Code, formerly the Building Code of Australia (BCA), has evolved over time to reflect best practices in building safety and accessibility. These standards draw on international building codes and are regularly updated to incorporate new research and address emerging safety concerns. The history of stair handrail regulations reflects a growing understanding of human factors, ergonomics, and the importance of universal design.
The core principle behind these regulations is simple: to minimize the risk of falls on stairs. Stairs are a common location for accidents, and handrails provide essential support and stability, particularly for children, the elderly, and people with disabilities. Compliance with the NCC ensures that stair handrails are robust enough to withstand anticipated loads and are positioned to offer optimal support.
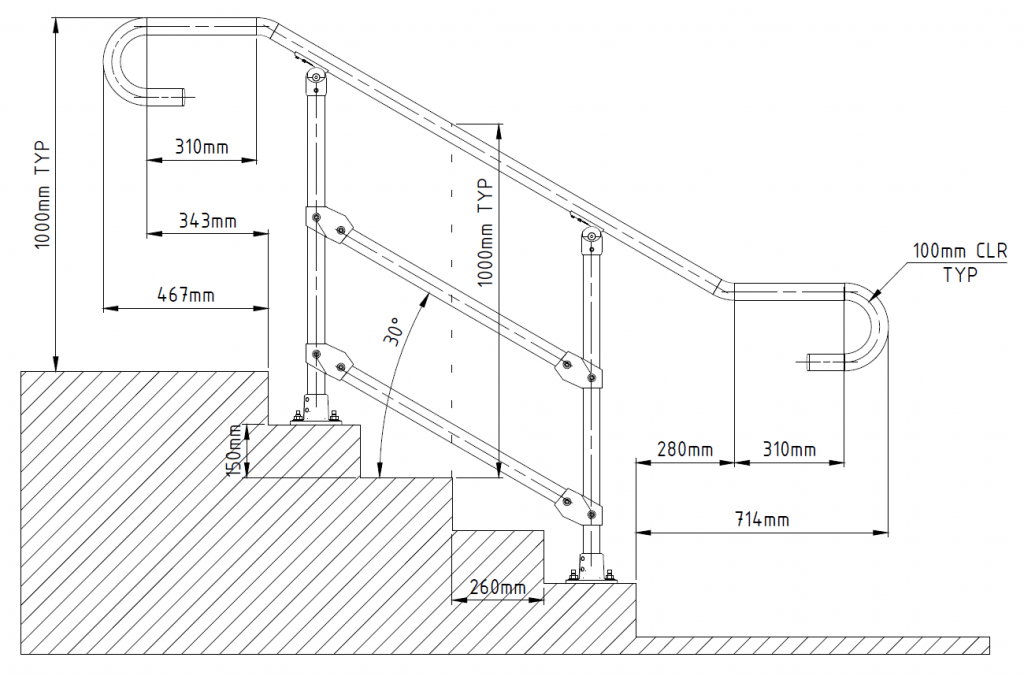
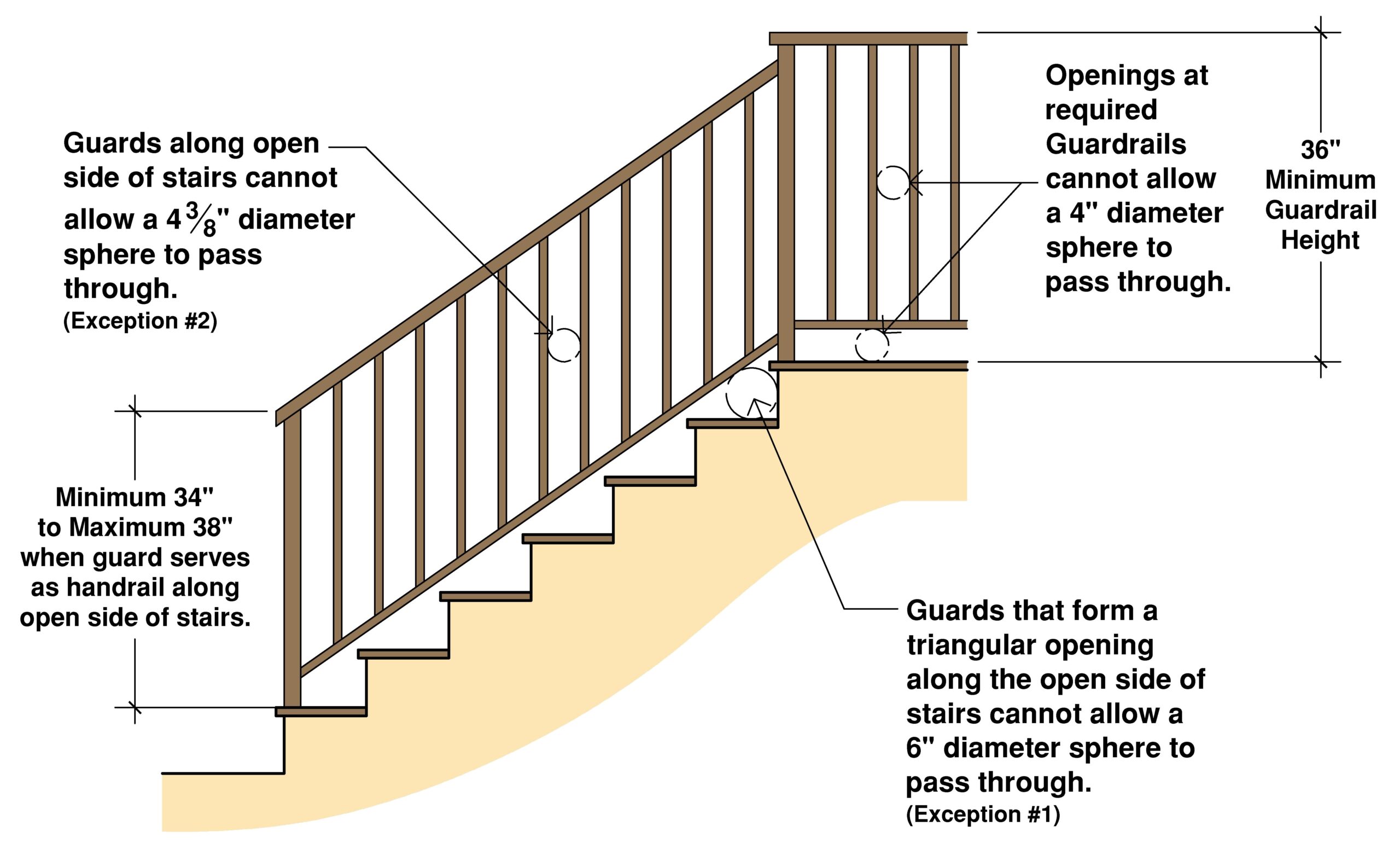
One key aspect of the Australian stair handrail regulations is the emphasis on continuity. Handrails must extend beyond the top and bottom steps, providing a continuous grip for users. This helps prevent stumbling at the beginning or end of the staircase. Regulations also specify minimum handrail heights and clearances to ensure accessibility for people of all heights and abilities.
The Building Code of Australia offers detailed guidelines for handrail dimensions, materials, and fixings. For example, it specifies minimum handrail diameters and requires handrails to be securely fixed to withstand specified loads. It also addresses handrail design for different types of staircases, including straight stairs, spiral stairs, and ramps.
One benefit of adhering to Australian stair handrail building codes is enhanced safety. Compliant handrails significantly reduce the risk of falls, protecting occupants and visitors from potential injuries.
Another advantage is improved accessibility. By following the NCC guidelines, builders can create staircases that are accessible to people of all ages and abilities, promoting inclusivity and independence.
Furthermore, compliance with the building code ensures legal compliance, avoiding potential penalties and legal issues. Meeting the requirements demonstrates a commitment to safety and responsible building practices.
A simple checklist for stair handrail compliance can include checking handrail height, continuity, strength, and material suitability. Verify that the handrail extends beyond the top and bottom steps and that clearances meet NCC requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Strict Adherence to the Building Code
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Potentially Higher Initial Costs |
| Improved Accessibility | Limited Design Flexibility in Some Cases |
| Legal Compliance | Requires Thorough Understanding of the Code |
Best practices for implementing Australian stair handrail regulations include consulting with qualified builders, using approved materials, conducting regular inspections, and staying updated on any changes to the NCC. Careful planning and attention to detail are essential for ensuring compliance and creating safe and accessible staircases.
Frequently asked questions about Australian stair handrail regulations often relate to handrail height requirements, allowable materials, and specific requirements for different staircase designs. Consulting the NCC and seeking expert advice can provide clarity on these matters.
Tips and tricks for complying with the building code include using prefabricated handrail systems that meet the NCC requirements, engaging a certified building inspector to verify compliance, and keeping detailed records of the construction process.
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to the Australian building code for stair handrails is paramount for creating safe and accessible environments. By prioritizing compliance, we can minimize the risk of falls, promote inclusivity, and ensure that our staircases are built to the highest safety standards. These regulations, while detailed, offer a clear pathway to creating stairs that are both functional and safe, ultimately contributing to a more secure and accessible built environment for everyone. Take the time to familiarize yourself with the NCC and consult with experts. Your diligence will contribute to a safer and more accessible world, one step at a time. Investing in compliant handrails is not just about meeting regulations; it's about investing in the well-being of everyone who uses our stairs.
Free legal advice online get your questions answered
Decoding caution do not use signs your guide to safety and compliance
The subtle art of outboard motor impeller renewal



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stair-handrail-and-guard-code-1822015-final-CJ-01-157768d7ac40439da36f9ba69faa00c6.png)