Understanding AC Relay Coil Operation
Ever wondered how a small electrical component can control powerful devices? The magic lies within the AC relay coil, a simple yet ingenious invention that forms the heart of many electrical systems. Understanding its operation opens up a world of possibilities for controlling and automating various electrical processes.
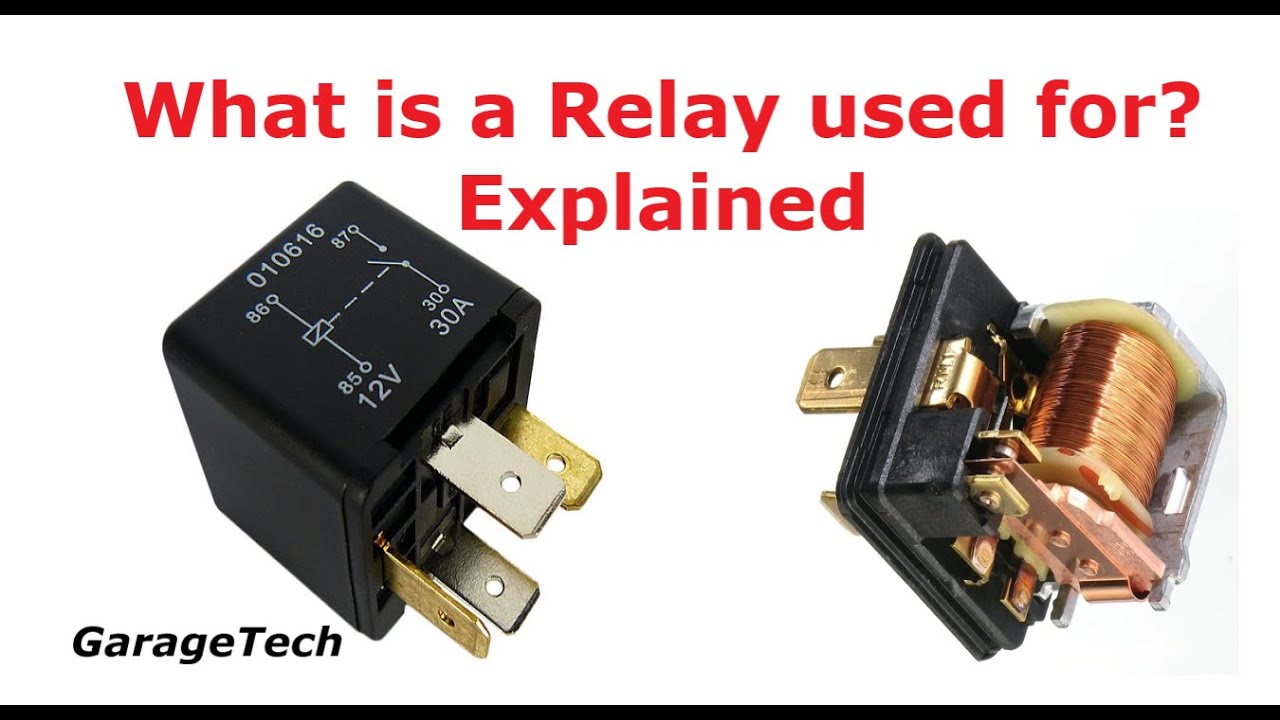
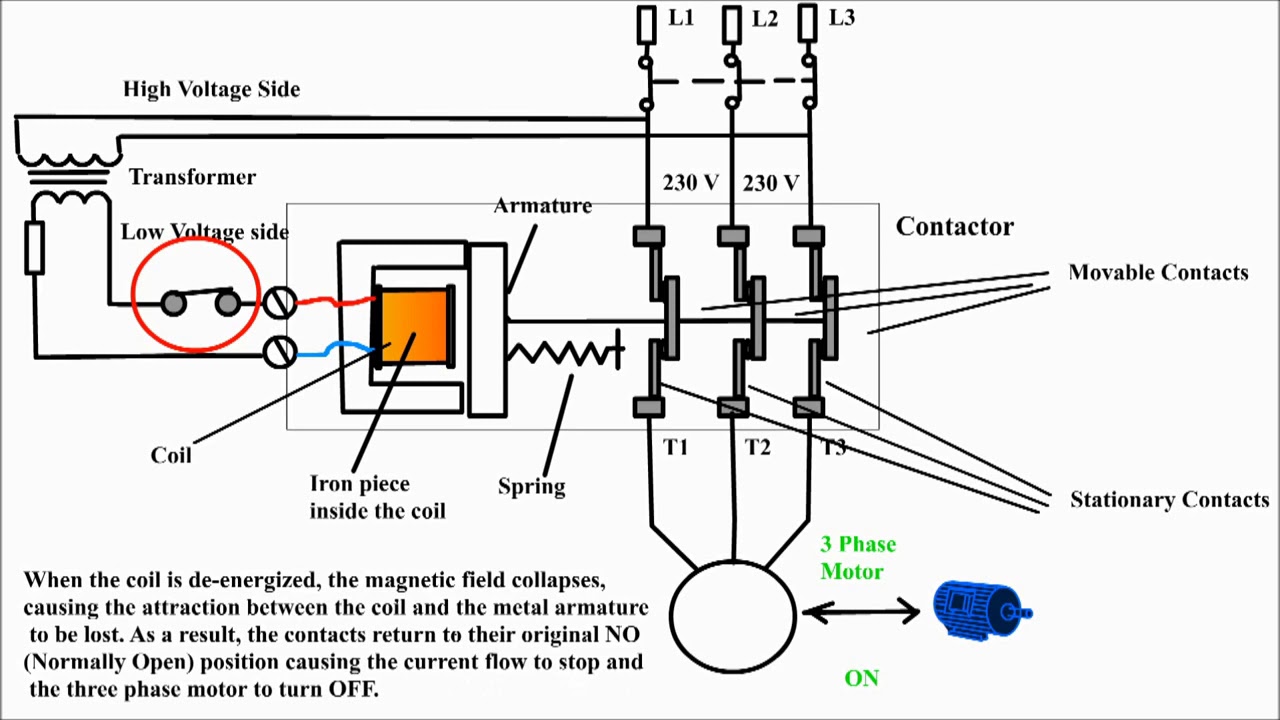
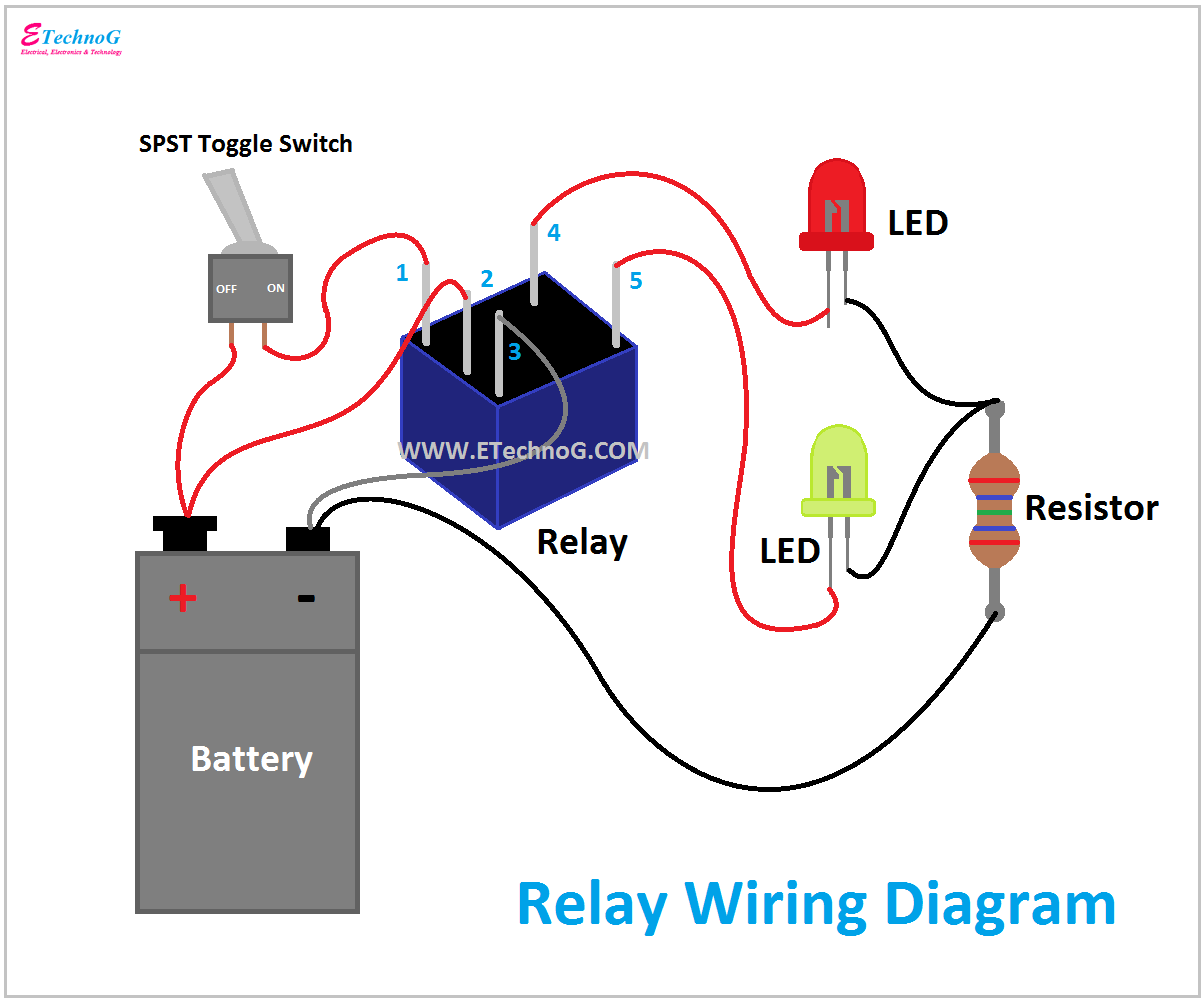
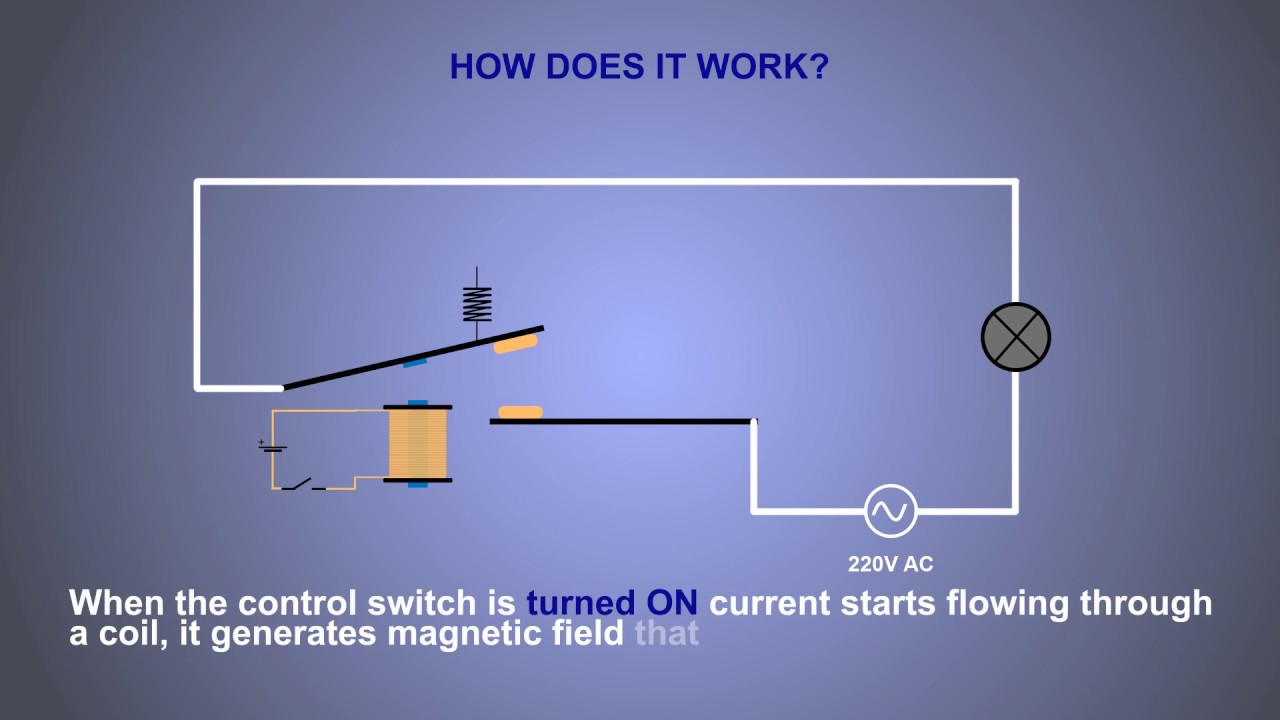
An AC relay coil's function is to create a magnetic field when an alternating current passes through it. This magnetic field attracts a metal armature, which in turn closes or opens electrical contacts, controlling the flow of electricity to another circuit. Think of it as an electrical switch controlled by magnetism.
The principle behind the AC relay coil is electromagnetism. When alternating current flows through the coil, it generates a fluctuating magnetic field. This changing magnetic field interacts with the armature, causing it to move and activate the switch contacts.
The AC relay's significance lies in its ability to control high-voltage or high-current circuits with a relatively small control current. This isolation between the control and controlled circuits enhances safety and efficiency.
One common issue with AC relay coils is coil burnout due to excessive current or voltage. Over time, the insulation within the coil can degrade, leading to shorts and malfunction. Proper selection and protection of the relay are crucial to prevent these issues.
Delving into the history, we find that relays have been around for over a century. Initially used in telegraphy, their application has expanded to countless areas, including industrial automation, automotive systems, and home appliances.
A practical example of an AC relay in action is in a heating system. A thermostat sends a small current to the relay coil, activating it and closing the contacts, which in turn supplies power to the heating element. When the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat interrupts the current to the relay coil, deactivating the relay and switching off the heater.
One benefit of using AC relays is their ability to isolate control circuits from high-power circuits. This separation improves safety by preventing high voltages from reaching the control system.
Another advantage is the ability to switch multiple circuits simultaneously with a single relay. This simplifies complex control systems and reduces the number of components required.
Furthermore, AC relays offer a cost-effective solution for controlling high-power loads. Their relatively simple design and readily available components contribute to their affordability.
Best practices for using AC relays include ensuring proper voltage and current ratings, providing adequate protection against surges and overloads, and using appropriate suppression techniques to minimize contact arcing.
Real examples include HVAC systems, motor control circuits, lighting control systems, and various automation processes in industrial settings.
Challenges associated with AC relay operation include contact wear, coil burnout, and chattering. Solutions involve using appropriate contact materials, providing adequate surge protection, and implementing proper snubber circuits.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Isolation between control and load circuits | Contact wear over time |
| Ability to switch multiple circuits | Potential for coil burnout |
| Cost-effective solution | Can be noisy due to mechanical switching |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the purpose of an AC relay coil? It energizes a magnetic field to switch contacts.
2. What causes coil burnout? Excessive current or voltage.
3. How does a relay control high-power circuits? With a small control current.
4. What is the role of the armature? It moves to close or open the contacts.
5. What are some applications of AC relays? HVAC, motor control, lighting control.
6. How can contact wear be minimized? Use appropriate contact materials.
7. What are snubber circuits used for? To reduce contact arcing.
8. What are some safety precautions for using relays? Proper voltage and current ratings, surge protection.
Tips and tricks for working with AC relays include using a multimeter to test coil resistance, inspecting contacts for wear, and ensuring proper ventilation to dissipate heat.
In conclusion, the AC relay coil is a fundamental component in various electrical systems. Its ability to control high-power circuits with a small control current makes it essential for automation and control applications. Understanding how AC relay coils work empowers us to design and maintain efficient and safe electrical systems. By following best practices and addressing potential challenges, we can leverage the power of this simple yet versatile component. From managing the comfort of our homes to driving complex industrial processes, the AC relay coil plays an indispensable role in shaping our modern world. Its simple operation, combined with its robust capabilities, ensures its continued relevance in an ever-evolving technological landscape. By continuing to learn and explore the intricacies of AC relay coils, we can unlock further potential for innovation and efficiency in electrical systems design and implementation. Exploring the workings of such fundamental components is key to appreciating the complex web of technology that surrounds us.
Unlock your inner artist mastering cool battle axe drawings
Neutralizing shampoo unveiled what it is and why you need it
Ace your nevada permit test smart prep strategies