Understanding Car Battery Voltage
Ever wondered about the silent power source that brings your car to life? It's your car battery, a seemingly simple box brimming with electrical potential. Understanding its voltage, especially when fully charged, is key to ensuring your vehicle starts reliably and powers all its electrical components.
A fully charged car battery's voltage is crucial for the overall health and functionality of your vehicle. But what exactly is the "right" voltage? And what can happen if it's off? Let's explore this fundamental aspect of car maintenance.
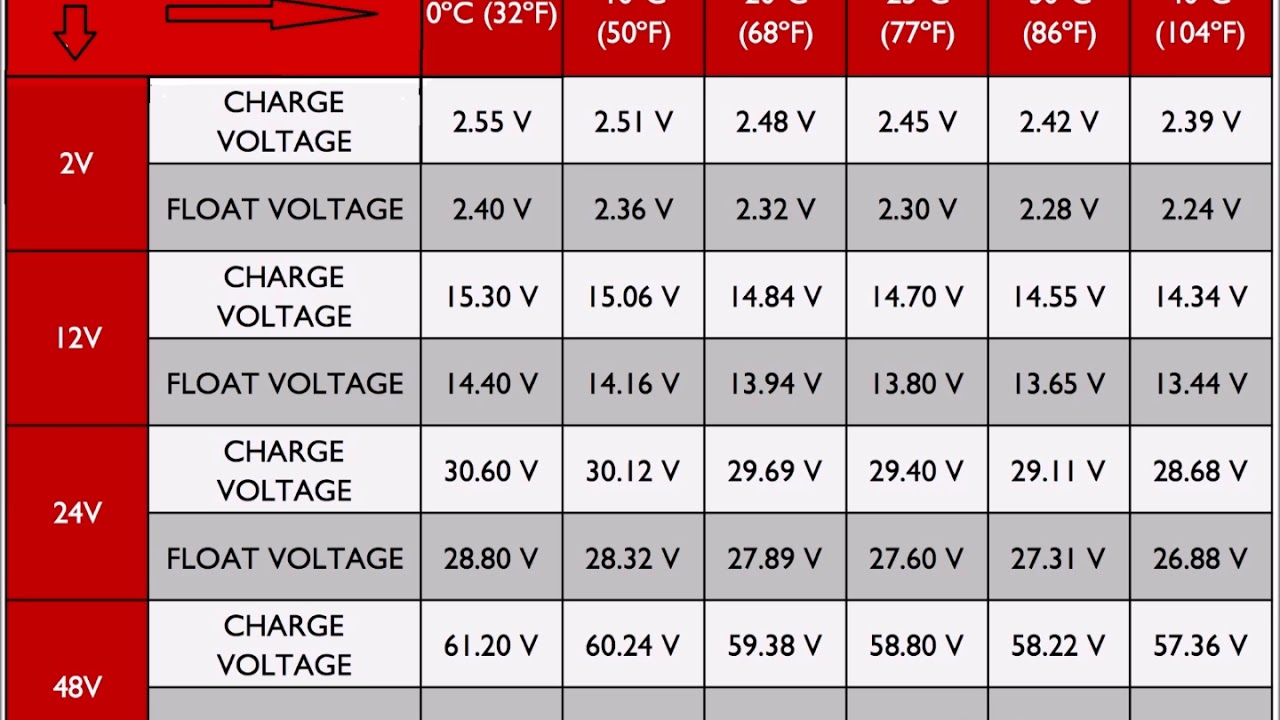
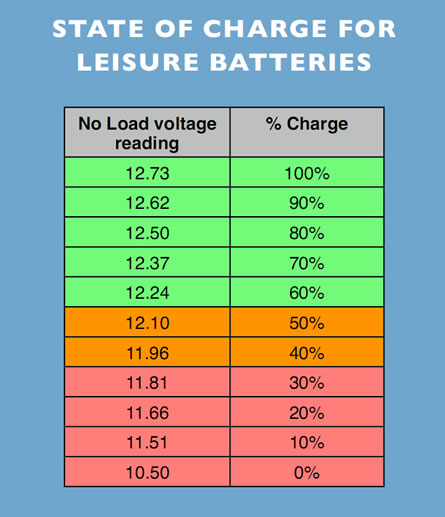
A typical 12-volt car battery, when fully charged, should register approximately 12.6 to 12.8 volts. This reading signifies that the battery is holding a healthy charge and is ready to deliver the necessary power to start your engine and operate accessories.
Variations in battery voltage can occur due to several factors. Temperature, for example, can influence the reading. A cold battery may show a lower voltage than a warm one, even if both are fully charged. The age of the battery also plays a role. Older batteries might struggle to hold a charge as effectively as newer ones.
Regularly checking your car battery voltage is a simple yet effective preventative maintenance practice. Early detection of voltage issues can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the life of your battery. A simple voltmeter can be used for this purpose.
The history of the car battery is intertwined with the development of the automobile itself. Early cars relied on hand cranks for starting, but as vehicles became more complex, a more reliable starting method was needed. The lead-acid battery, invented in the mid-19th century, eventually became the standard power source for starting engines.
The importance of a fully charged car battery is undeniable. It provides the initial surge of electricity needed to crank the engine, power the ignition system, and supply power to various electronic components, even when the engine is off. A healthy battery ensures reliable starting and smooth operation of all electrical systems.
One of the main issues related to car battery voltage is overcharging or undercharging. Overcharging can damage the battery's internal components, while undercharging can lead to sulfation, a buildup of lead sulfate crystals that reduces the battery's capacity to hold a charge.
A simple example to illustrate the importance of proper voltage is the starting process. When you turn the key, the starter motor draws a large amount of current from the battery. If the battery voltage is too low, the starter motor might not have enough power to turn the engine over, resulting in a no-start situation.
Benefit 1: Reliable Starting - A fully charged battery ensures your car starts reliably every time, eliminating the frustration of a dead battery.
Benefit 2: Optimal Performance of Electrical Systems - A properly charged battery provides consistent power to all electrical components, such as lights, radio, and power windows.
Benefit 3: Extended Battery Lifespan - Maintaining the correct voltage through proper charging practices helps prolong the life of your car battery.
Action Plan for Maintaining Car Battery Voltage:
1. Regularly check your battery voltage using a voltmeter.
2. Ensure your car's charging system is functioning correctly.
3. Limit short trips, as they can prevent the battery from fully recharging.
4. Clean battery terminals to ensure good electrical connections.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Proper Car Battery Voltage
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reliable engine starting | Requires regular monitoring |
| Optimal electrical system performance | Susceptible to extreme temperatures |
| Extended battery lifespan | Can be damaged by overcharging or deep discharging |
FAQs:
1. What is the normal voltage of a fully charged car battery? Around 12.6 to 12.8 volts.
2. How often should I check my car battery voltage? Monthly is recommended.
3. What causes a car battery to lose its charge? Several factors including parasitic drains, old age, extreme temperatures, and faulty charging systems.
4. Can I jump-start a car with a low battery voltage? Yes, but address the underlying cause of the low voltage.
5. How long does a car battery typically last? 3 to 5 years on average.
6. What are signs of a failing car battery? Slow engine cranking, dim headlights, and electrical malfunctions.
7. How can I test my car battery? Using a multimeter or having it tested at an auto parts store.
8. Should I disconnect my car battery if I'm not using the vehicle for an extended period? Yes, this can prevent the battery from draining.
Tips for Maintaining Car Battery Voltage:
Avoid leaving lights and accessories on when the engine is off.
Park in a garage or shaded area during extreme temperatures.
Have your charging system inspected regularly.
In conclusion, understanding and maintaining the correct voltage on a fully charged car battery is essential for the reliability and longevity of your vehicle. Regularly checking the voltage, understanding the factors that influence it, and practicing proper maintenance will ensure your car starts reliably every time and its electrical systems perform optimally. Taking proactive steps to maintain your car battery will ultimately save you time, money, and the frustration of unexpected breakdowns. Don't wait until your car won't start to think about your battery. Take a few minutes today to check its voltage and ensure it's in good health. This small investment of time can pay big dividends in the long run.
Kuromi desktop wallpaper hd 4k level up your screen
Unlocking the best toyota rav4 years a comprehensive guide
Conquering the creepy crawlies a comprehensive guide to pest control