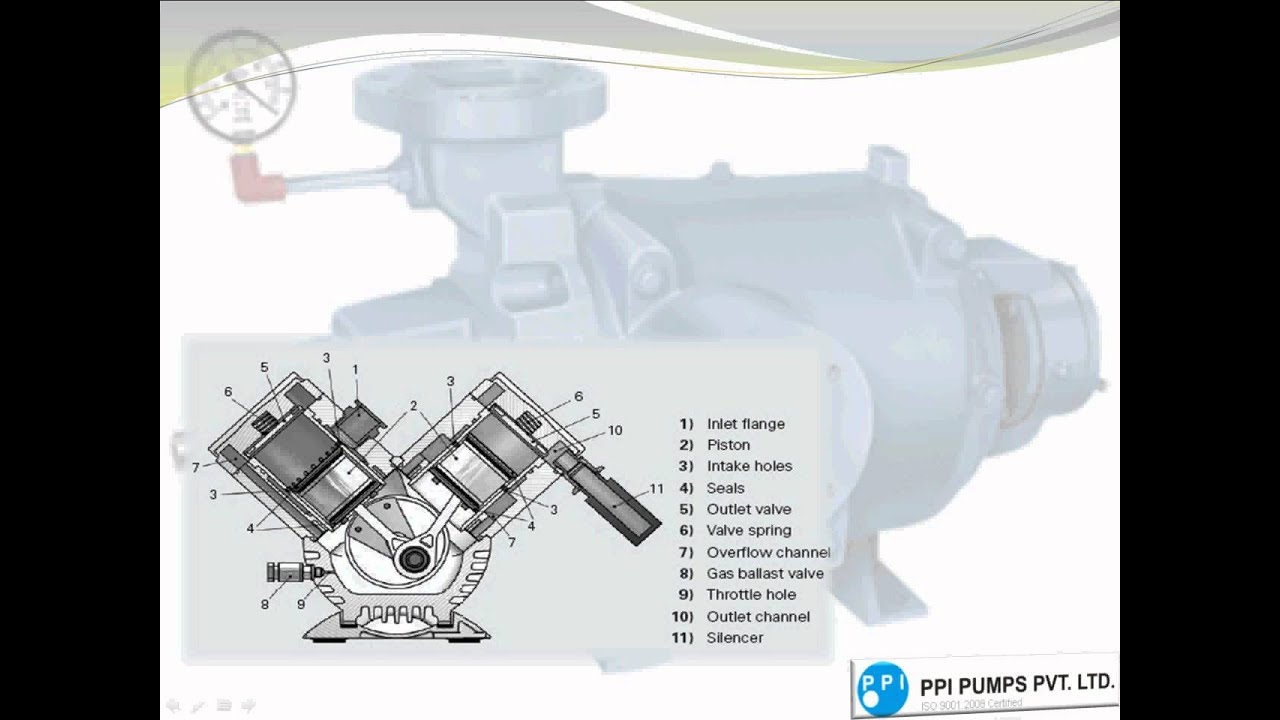
Understanding Small Engine Vacuum Fuel Pumps
Ever wonder how your lawnmower sips fuel so efficiently? Or how that little outboard motor keeps chugging along? The secret often lies in a small but mighty component: the vacuum fuel pump. These unassuming devices are the heart of many small engine fuel systems, ensuring a steady flow of gasoline to keep things running smoothly.
Small engine vacuum fuel pumps are mechanical marvels that utilize engine vacuum pressure to draw fuel from the tank and deliver it to the carburetor. Unlike electric fuel pumps found in cars, these pumps are simpler, often more reliable, and perfectly suited for the demands of smaller engines. Understanding how these pumps function is essential for anyone who owns and maintains outdoor power equipment.
The principle behind a vacuum fuel pump is elegantly simple. As the engine runs, it creates a vacuum in the intake manifold. This vacuum is channeled to the pump through a pulse line. Inside the pump, a diaphragm responds to the fluctuating vacuum pressure, creating a pumping action. This pumping action draws fuel from the tank through an inlet valve and pushes it towards the carburetor through an outlet valve. The consistent pulsing ensures a continuous supply of fuel as long as the engine is running.
Vacuum fuel pumps have a long history, dating back to the early days of internal combustion engines. Their simple design and reliability made them a popular choice for small engines. Before the widespread use of vacuum fuel pumps, gravity-fed fuel systems were common, but these systems had limitations, especially in applications requiring varying angles of operation, such as lawnmowers and chainsaws. The vacuum fuel pump offered a more robust and versatile solution.
These pumps are crucial for the proper function of numerous small engines found in lawnmowers, chainsaws, generators, tillers, and outboard motors. Without a reliable fuel delivery system, these engines would sputter, stall, or fail to start altogether. Understanding the operation of these pumps empowers owners to troubleshoot common issues, perform basic maintenance, and keep their equipment running smoothly.
A common problem with vacuum fuel pumps is a ruptured diaphragm. This thin rubber membrane is essential for the pump’s operation, and if it cracks or tears, the pump will lose its ability to draw fuel. Another issue can be clogged fuel lines or filters. Debris in the fuel can restrict flow and starve the engine of gasoline. Checking and replacing fuel filters regularly is vital for maintaining optimal fuel pump performance. A third potential problem involves the pulse line, which connects the engine to the pump. If this line becomes disconnected, kinked, or cracked, the vacuum signal won't reach the pump, disrupting fuel delivery.
Benefits of Vacuum Fuel Pumps
1. Simplicity: Vacuum fuel pumps have fewer moving parts than electric fuel pumps, making them less prone to failure and easier to repair.
2. Cost-effectiveness: These pumps are generally inexpensive to purchase and maintain compared to electric fuel pump systems.
3. Reliability: With their simple design and robust construction, vacuum fuel pumps offer reliable performance in demanding small engine applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vacuum Fuel Pumps
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplicity and ease of repair | Limited performance at high altitudes |
| Cost-effective | Susceptible to diaphragm failure |
| Reliable in most conditions | Performance can be affected by variations in engine vacuum |
Troubleshooting Checklist
1. Check fuel lines for kinks or blockages.
2. Inspect the fuel filter for clogging.
3. Examine the pulse line for damage or disconnection.
4. Test the fuel pump for proper vacuum and pressure.
FAQ
1. How does a small engine vacuum fuel pump work? It uses engine vacuum to create a pumping action that draws fuel from the tank.
2. What are common problems with these pumps? Ruptured diaphragms, clogged fuel lines, and faulty pulse lines are common issues.
3. How do I test a vacuum fuel pump? You can use a vacuum gauge to test the pump's ability to create suction.
4. How often should I replace the fuel filter? It's recommended to replace the fuel filter at least once a year or more frequently if operating in dusty or dirty conditions.
5. Can I repair a ruptured diaphragm? While diaphragm repair kits are available, replacing the entire pump is often the most reliable solution.
6. What causes a fuel pump to fail? Age, wear and tear, and fuel contamination are common causes of fuel pump failure.
7. How do I prevent fuel pump problems? Regular maintenance, including fuel filter replacement and fuel system cleaning, can prevent many fuel pump issues.
8. Where can I find a replacement vacuum fuel pump? Small engine repair shops, online retailers, and hardware stores typically carry replacement fuel pumps.
In conclusion, the small engine vacuum fuel pump is a vital component in a wide range of outdoor power equipment. Understanding its operation, troubleshooting common problems, and performing basic maintenance will keep your engines running smoothly. By taking the time to learn about this essential part, you'll be well-equipped to handle any fuel delivery challenges and enjoy the reliable performance of your small engines for years to come. Don't underestimate the power of this small but mighty device – it's the key to keeping your outdoor equipment humming along.
Mastering boat electrical systems your guide to marine battery wiring
Ultimate guide to audi rs3 8v wallpapers
Suns sting decoding the itchy rash