Unlocking the Power of 3-Cylinder Turbo Engines
In the ever-evolving world of automotive technology, the quest for efficiency and performance has led to innovative engine designs. One such marvel is the 3-cylinder turbo engine. But what exactly is a 3-cylinder turbo engine, and why is it gaining popularity?
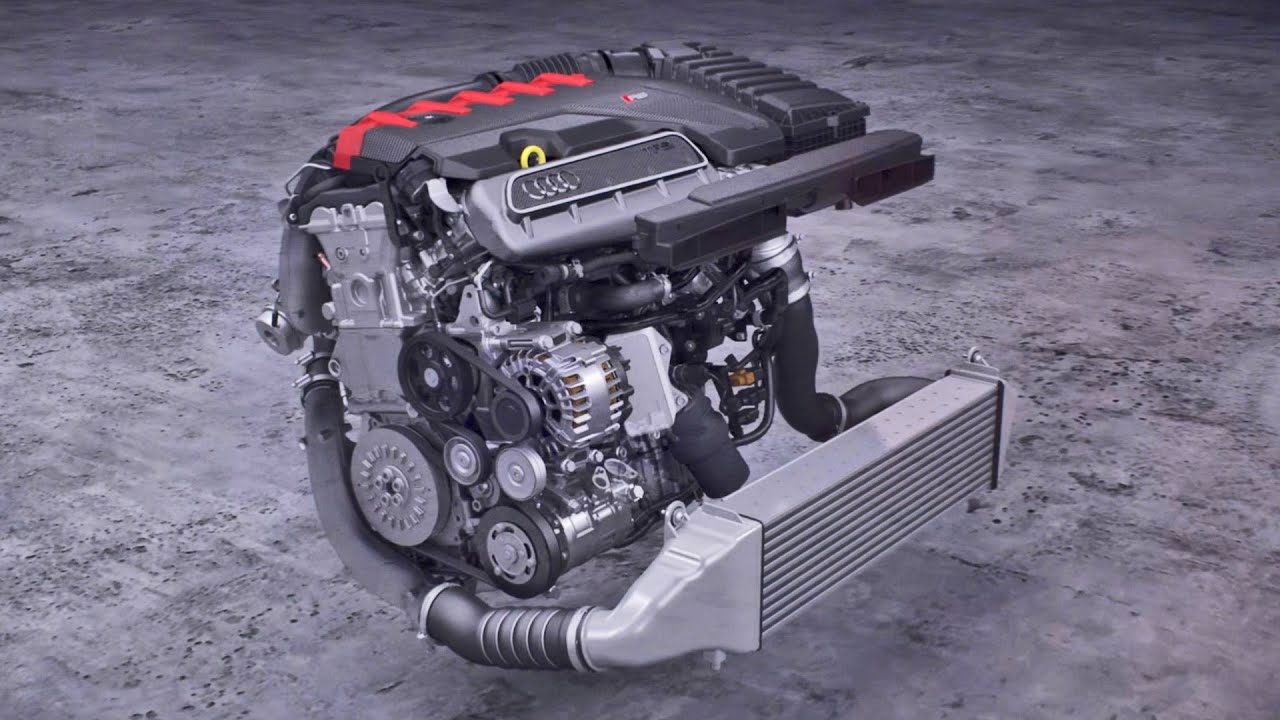
A 3-cylinder turbo engine, as the name suggests, is an internal combustion engine with three cylinders arranged in a line or occasionally in a triangular configuration. The "turbo" part refers to the turbocharger, a device that forces more air into the engine, boosting power output beyond what its small size might suggest. This combination of fewer cylinders and forced induction creates a surprisingly potent and efficient powerplant.
Imagine a small but mighty engine capable of delivering impressive power while sipping fuel. This describes the essence of a 3-cylinder turbo. This technology allows automakers to achieve a delicate balance between performance and fuel economy, a critical factor in today's automotive landscape.
The rise of the three-cylinder turbo engine has been driven by increasingly stringent emissions regulations and the demand for better fuel economy. These engines are inherently lighter and more compact than their four-cylinder counterparts, which further contributes to improved efficiency. The turbocharger compensates for the reduced displacement, delivering power comparable to larger, naturally aspirated engines.
Understanding the workings of a 3-cylinder turbo engine begins with grasping the basic principles of internal combustion. Like all gasoline engines, it relies on a four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. The turbocharger increases the intake air pressure, leading to a more powerful explosion during combustion and thus increased power output. This allows a smaller engine to perform like a larger one.
The history of 3-cylinder engines dates back to the early 20th century, but their use in automobiles was limited due to inherent vibration issues. Advances in engine balancing and mounting technologies have largely mitigated these problems, paving the way for their resurgence. The addition of a turbocharger further enhanced their performance, making them a viable option for a wide range of vehicles.
One of the key benefits of these engines is their fuel efficiency. With fewer cylinders and less displacement, they consume less fuel, especially during city driving or low-load situations. Another advantage is their reduced weight and compact size, which contributes to improved handling and vehicle dynamics.
However, 3-cylinder turbo engines can also present certain challenges. One common issue is turbo lag, the delay between pressing the accelerator and feeling the boost of power. Careful turbocharger selection and engine management calibration can minimize this effect.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3-Cylinder Turbo Engines
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved Fuel Efficiency | Potential for Turbo Lag |
| Reduced Weight and Size | Noise and Vibration (though significantly improved) |
| Lower Emissions | Limited Towing Capacity Compared to Larger Engines |
Frequently Asked Questions about 3-Cylinder Turbo Engines:
1. Are 3-cylinder turbo engines reliable? Yes, with proper maintenance, they can be just as reliable as other engine configurations.
2. Are they noisy? While they can be slightly noisier than larger engines, modern designs have greatly reduced noise and vibration.
3. Do they have enough power? Yes, thanks to the turbocharger, they can produce surprising amounts of power for their size.
4. Are they good for highway driving? Yes, they can perform well on the highway, offering a balance of power and fuel efficiency.
5. Are they expensive to maintain? Maintenance costs are generally comparable to other engine types.
6. What kind of cars use them? A variety of cars, from small city cars to compact SUVs, use 3-cylinder turbo engines.
7. How long do they last? With proper care, they can last just as long as larger engines, often exceeding 150,000 miles.
8. What is turbo lag? Turbo lag is the delay between pressing the accelerator and the turbocharger spooling up and delivering boost.
Real-world examples of cars using 3-cylinder turbo engines include the Ford Fiesta, the Mini Cooper, and certain models of the BMW i8. These vehicles demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of this technology.
In conclusion, the 3-cylinder turbo engine represents a significant advancement in automotive engineering. It offers a compelling blend of power, efficiency, and reduced emissions. While some challenges remain, ongoing developments are continually refining this technology, making it a key player in the future of transportation. Understanding the benefits and limitations of 3-cylinder turbo engines empowers consumers to make informed choices in the ever-expanding automotive market. Embrace the power of small but mighty, and experience the future of driving today.
Unlocking the night h e b part time stocking opportunities
Lost your toyota rav4 keys your guide to key fob replacement
The enduring appeal of disney princess imagery